Noncollinear spin structure in Fe3+xCo3−xTi2 (x = 0, 2, 3) from neutron diffraction
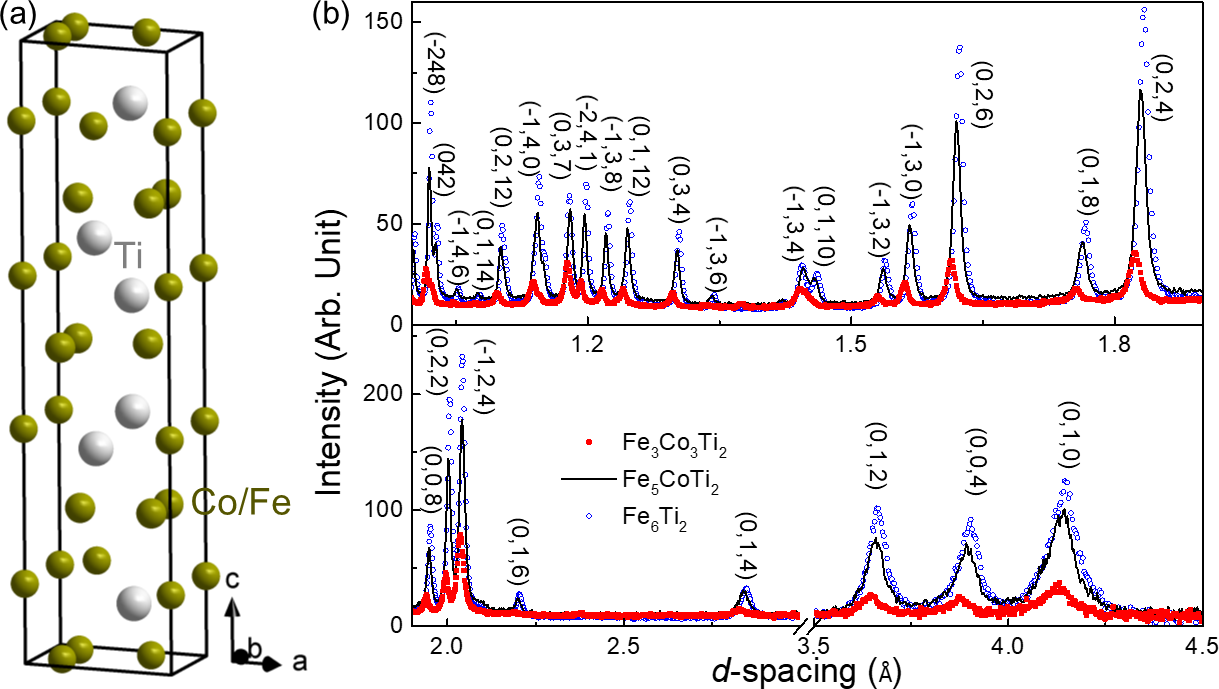
Neutron powder diffraction has been used to investigate the spin structure of the hard-magnetic alloy hexagonal Fe3+xCo3−xTi2 (x = 0, 2, 3). Projections of the magnetic moment onto both the crystalline c axis and the basal plane were observed. The corresponding misalignment angle exhibits a nonlinear decrease with x, which we explain as a micromagnetic effect caused by Fe-Co site disorder.
See more details: Phys. Rev. Mat. 3, 064403 (2019).
Anti-site mixing and magnetic properties of Fe3Co3Nb2 studied via neutron powder diffraction
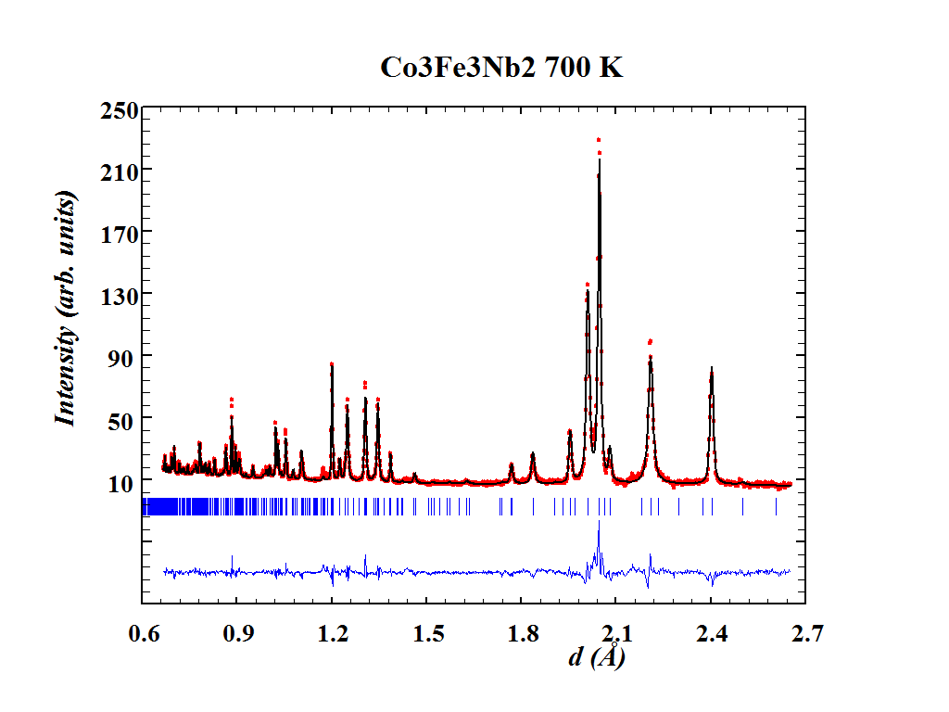
The rare-earth-free intermetallic compound Fe3Co3Nb2, which has recently been demonstrated to have potentially high magnetic anisotropy, using temperature-dependent neutron powder diffraction. We found from the structural refinement of the paramagnetic state and the substantial magnetic contribution to the diffuse scattering in the ferromagnetic state, the Fe/Co anti-site mixing is so strong that the site occupation for Fe and Co is almost random, which causes that he projection of the magnetic moments to be non-zero along the c axis and in the a–b plane.
See more details: J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 50, 025002 (2017)