Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in conducting NiCo2O4 films from spin-lattice coupling
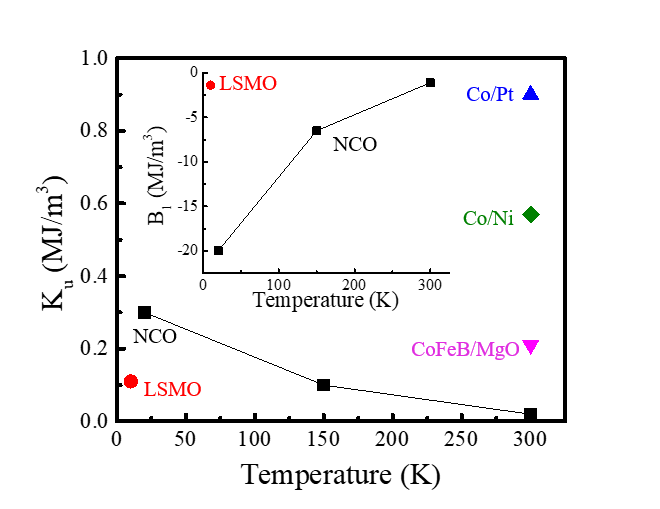 High perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), a property needed for nanoscale spintronic applications, is rare in oxide conductors. We report the observation of a PMA up to 0.23 MJ/m3 in modestly strained (–0.3%) epitaxial NiCo2O4 films which are room-temperature ferrimagnetic conductors.
See more details: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 101, 014413 (2020).
High perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), a property needed for nanoscale spintronic applications, is rare in oxide conductors. We report the observation of a PMA up to 0.23 MJ/m3 in modestly strained (–0.3%) epitaxial NiCo2O4 films which are room-temperature ferrimagnetic conductors.
See more details: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 101, 014413 (2020).
|
Structural phase diagram and magnetic properties of Sc-substituted rare earth ferrites R1−xScxFeO3 (R = Lu, Yb, Er, and Ho)
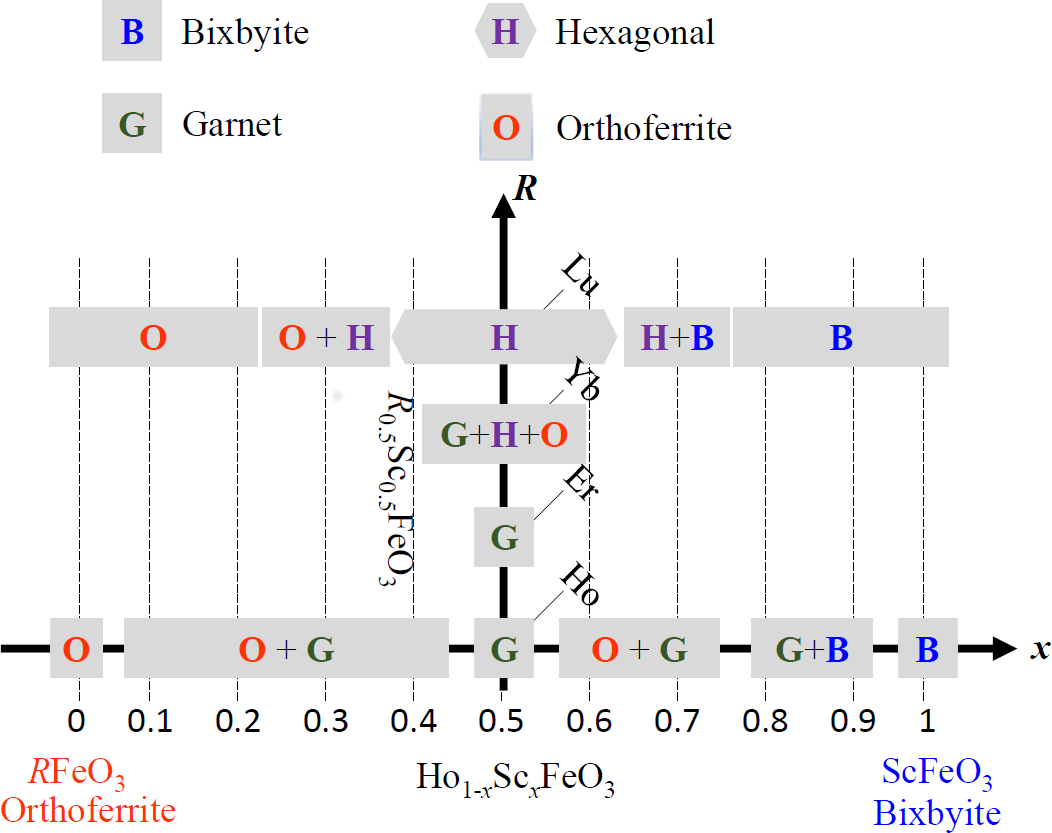 Substituting rare earth with Sc in RFeO3 results in rich structural phases including orthorhombic, hexagonal, bixbyite, and garnet, as reported in this work.
See more details: J. Appl. Phys. 125, 244101 (2019).
Substituting rare earth with Sc in RFeO3 results in rich structural phases including orthorhombic, hexagonal, bixbyite, and garnet, as reported in this work.
See more details: J. Appl. Phys. 125, 244101 (2019).
|
Tuning the Néel Temperature of Hexagonal Ferrites by Structural Distortion
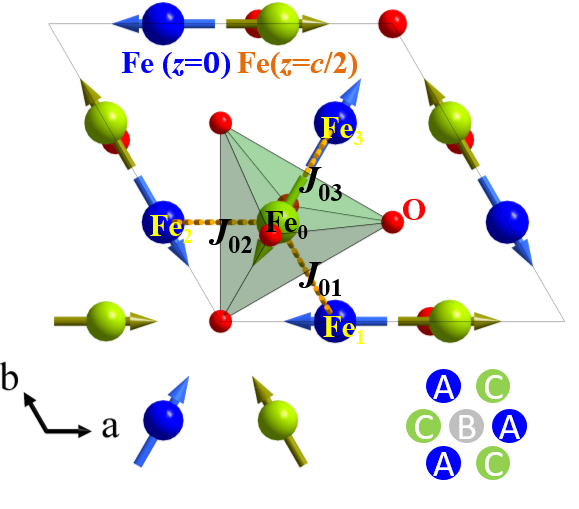 Neutron diffraction on the thin film hexagonal ferrites reveals that working temperature of hexagonal multiferroic ferrites can be increased by reducing size of the R atoms in h-RFeO3 and proves the record-high Neel temperature in h-ScFeO3. The work provides the insight into optimizing hexagonal ferrites by increasing the K3-distortion, which hosts great potential for applications, such as sensors, microwave devices, energy harvesting and energy-efficient recording technologies.
See more details: Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 237203 (2018).
Neutron diffraction on the thin film hexagonal ferrites reveals that working temperature of hexagonal multiferroic ferrites can be increased by reducing size of the R atoms in h-RFeO3 and proves the record-high Neel temperature in h-ScFeO3. The work provides the insight into optimizing hexagonal ferrites by increasing the K3-distortion, which hosts great potential for applications, such as sensors, microwave devices, energy harvesting and energy-efficient recording technologies.
See more details: Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 237203 (2018).
|
Nanostructural origin of semiconductivity in epitaxial NiCo2O4/Al2O3 thin films
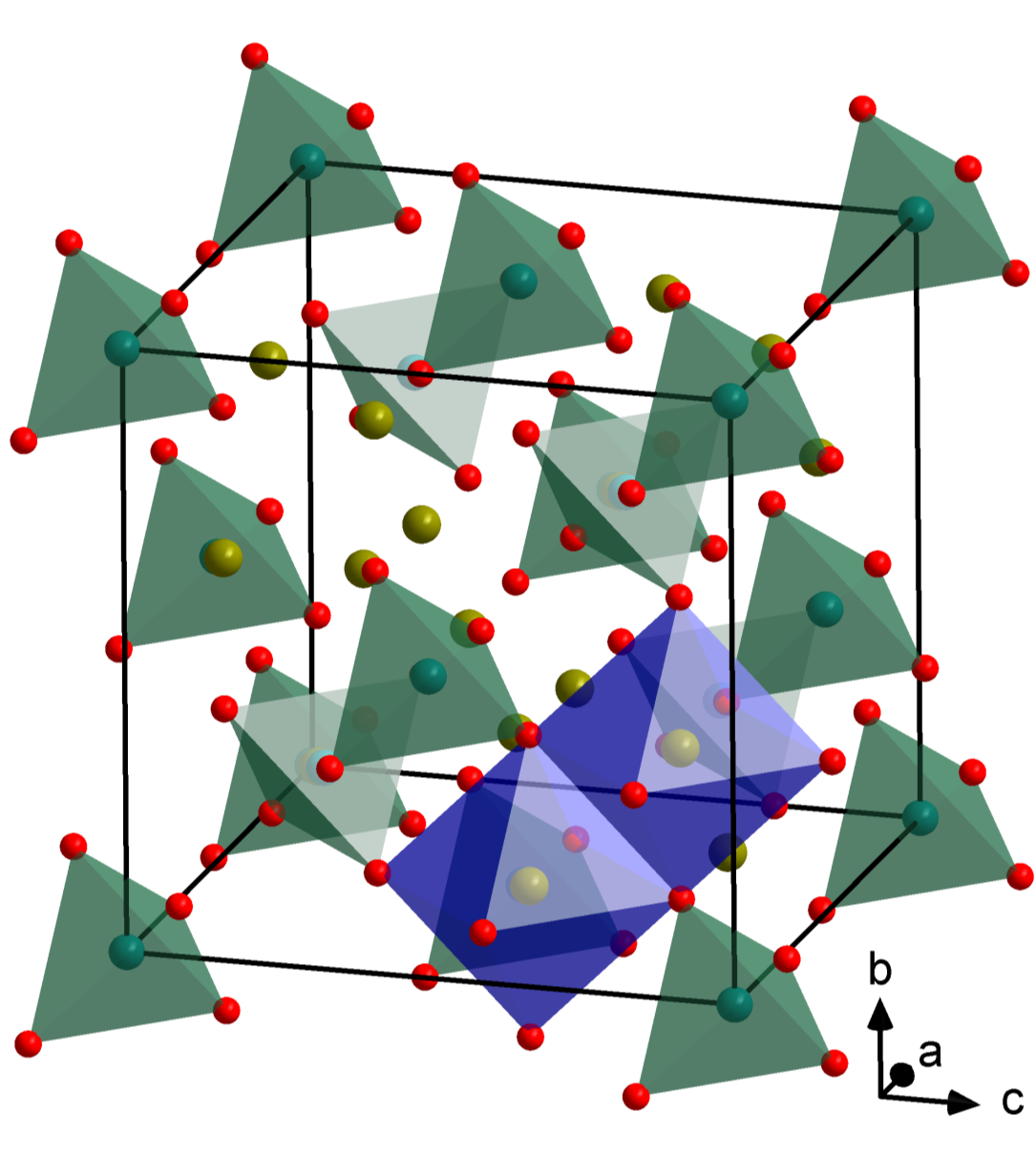 NiCo2O4 has been revealed as metallic in epitaxial NiCo2O4/MgAl2O4 thin films. However, even with the same optimal growth condition, the NiCo2O4/Al2O3 films are always semiconducting. Using a suite of characterization such as magnetometer, transport, x-ray diffraction, as well as the change of NiCo2O4 upon annealing, we found that the structural disorder caused by the difference between the substrate and the film structures is the origin of the semiconductivity and the large magnetoresistance.
See more details: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51, 145308 (2018).
NiCo2O4 has been revealed as metallic in epitaxial NiCo2O4/MgAl2O4 thin films. However, even with the same optimal growth condition, the NiCo2O4/Al2O3 films are always semiconducting. Using a suite of characterization such as magnetometer, transport, x-ray diffraction, as well as the change of NiCo2O4 upon annealing, we found that the structural disorder caused by the difference between the substrate and the film structures is the origin of the semiconductivity and the large magnetoresistance.
See more details: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51, 145308 (2018).
|
Ferrimagnetism in h-RFeO3
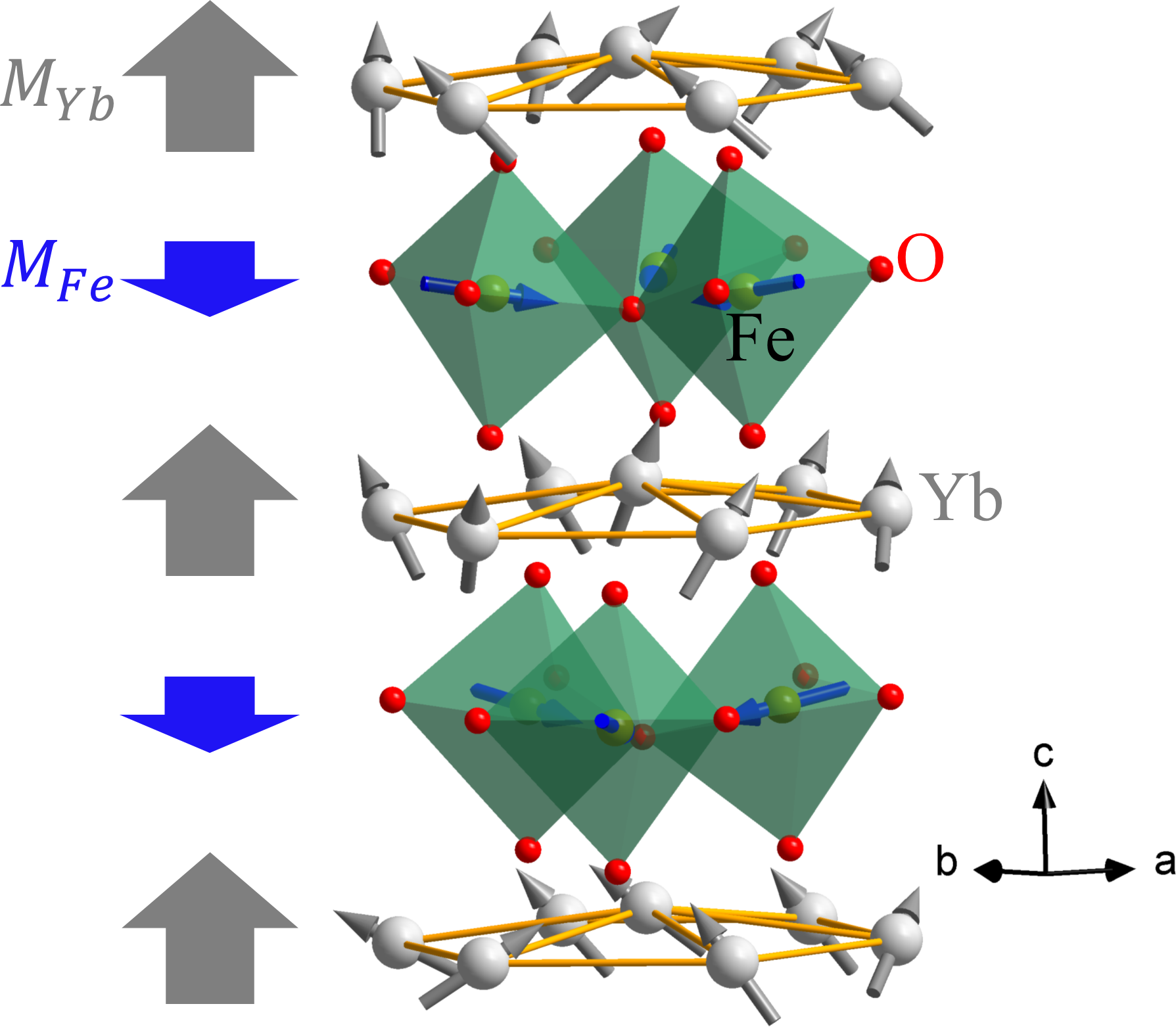 Magnetic interactions between Yb and Fe in h-YbFeO3 have been studied. We found that Yb moments follow Fe moments paramagnetically with anti-alignment. At 80 K (moment compensation temperature), the Yb moments and the Fe moments cancel each other. See more details: Phys. Rev. B 95, 224428 (2017).
Magnetic interactions between Yb and Fe in h-YbFeO3 have been studied. We found that Yb moments follow Fe moments paramagnetically with anti-alignment. At 80 K (moment compensation temperature), the Yb moments and the Fe moments cancel each other. See more details: Phys. Rev. B 95, 224428 (2017).
|
Magnetism and epitaxy of h-RFeO3/Fe3O4
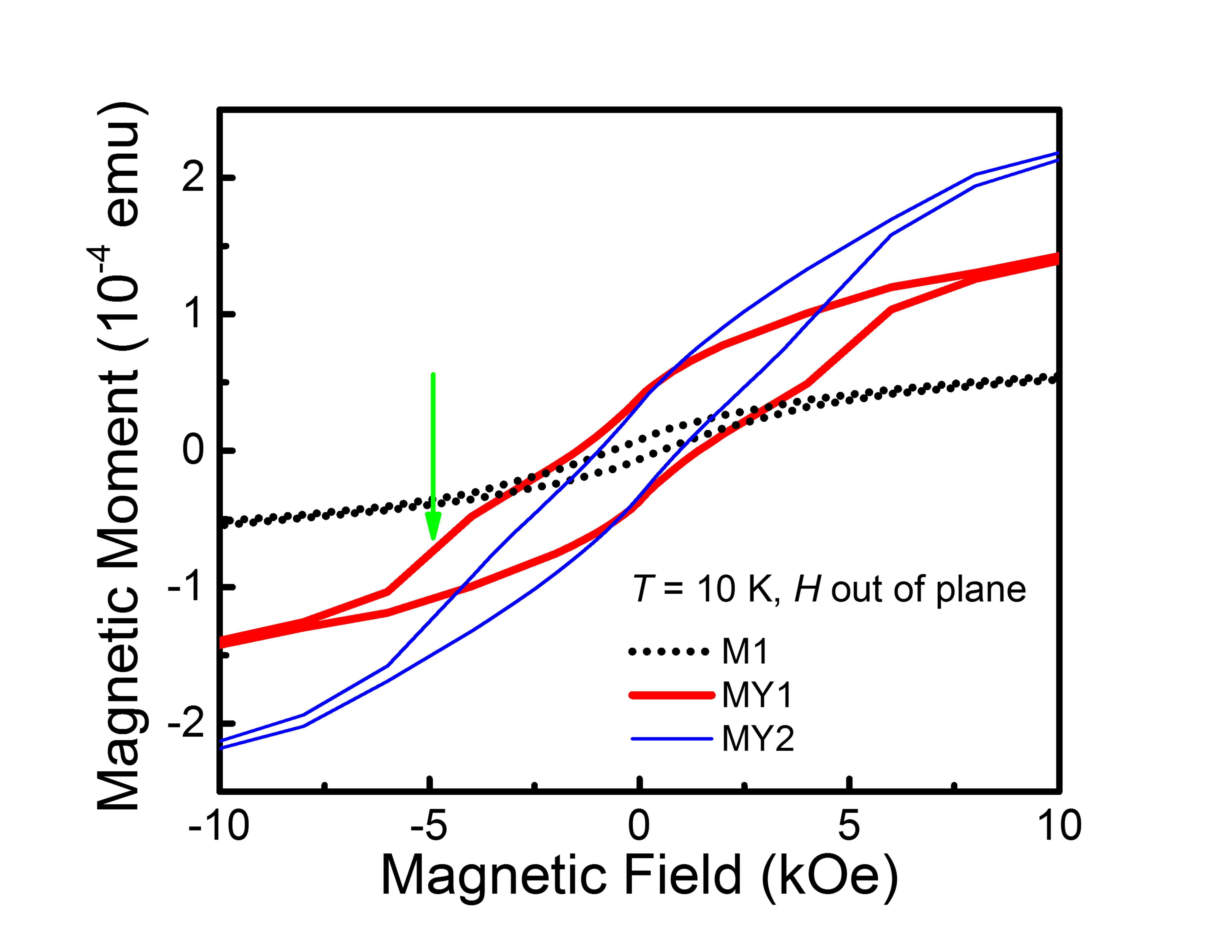 We have found that h-RFeO3(001)/Fe3O4(111) may form well-defined interface due to good match of lattice constant. It is also interesting that the magnetic easy axis of the two layers are perpendicular to each other: easy axis of Fe3O4 layer in (111) plane; easy axis of h-RFeO3 layer along [001] direction. See more details: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 29, 164001 (2017).
We have found that h-RFeO3(001)/Fe3O4(111) may form well-defined interface due to good match of lattice constant. It is also interesting that the magnetic easy axis of the two layers are perpendicular to each other: easy axis of Fe3O4 layer in (111) plane; easy axis of h-RFeO3 layer along [001] direction. See more details: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 29, 164001 (2017).
|
Strain effect in h-LuFeO3 measured using restrained thermal expansion
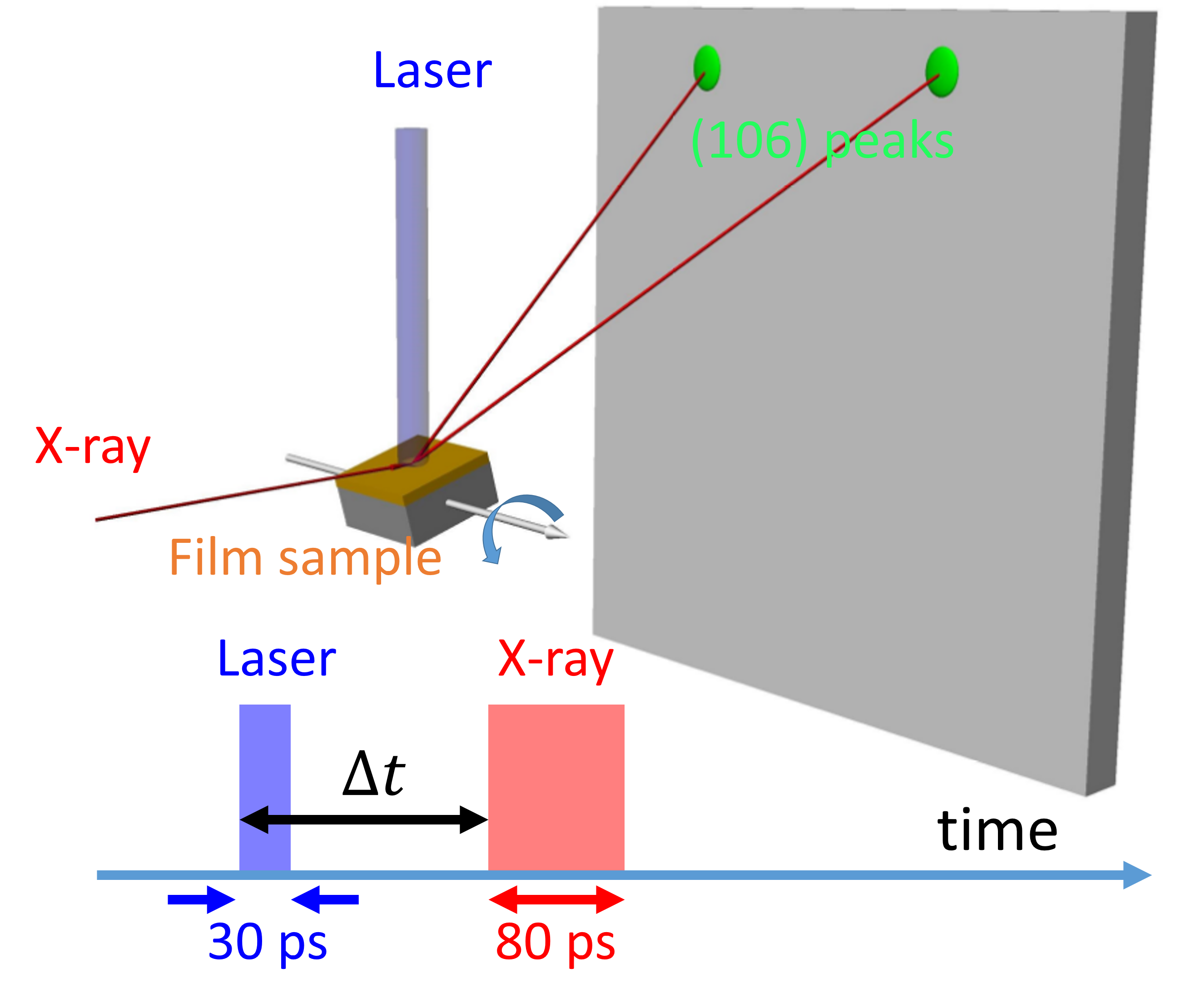 The effect of biaxial strain in hexagonal ferrites has been challenging to tackle due to the experimental difficulties. Employing the restrained thermal expansion method, we successfully measured the strain effect. The results show that the compressive strain enhances the K3 lattice distortion. Our first principle calculation indicate that the compressive strain also enhances the electric polarization bu reduces the magnetic polarization. See more details: Phys. Rev. B. 95, 094110 (2017)
The effect of biaxial strain in hexagonal ferrites has been challenging to tackle due to the experimental difficulties. Employing the restrained thermal expansion method, we successfully measured the strain effect. The results show that the compressive strain enhances the K3 lattice distortion. Our first principle calculation indicate that the compressive strain also enhances the electric polarization bu reduces the magnetic polarization. See more details: Phys. Rev. B. 95, 094110 (2017)
|
Kinetics and intermediate phases in epitaxial growth of Fe3O4 films from deposition and thermal reduction
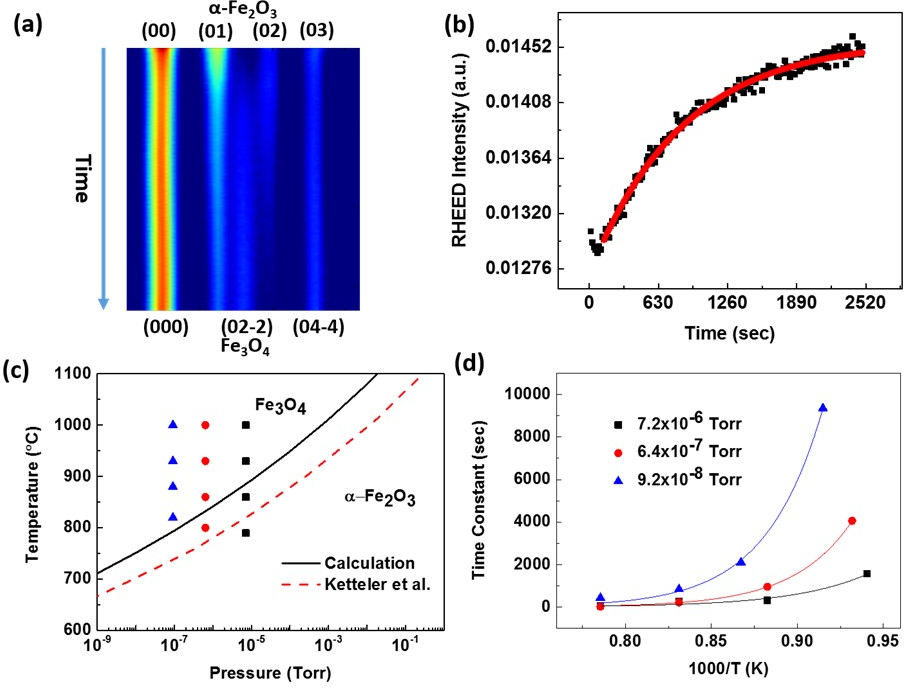 Fe3O4 is arguably the oldest magnetic material known to the human beings. Yet new functionalities are being exploited constantly. Using the thermal reduction method, we have successfully grown Fe3O4 thin films of flat surface (atomic terrace). See more details: Journal of Applied Physics 120, 085313 (2016), arXiv
Fe3O4 is arguably the oldest magnetic material known to the human beings. Yet new functionalities are being exploited constantly. Using the thermal reduction method, we have successfully grown Fe3O4 thin films of flat surface (atomic terrace). See more details: Journal of Applied Physics 120, 085313 (2016), arXiv
|
Phase separation in LuFeO3 films
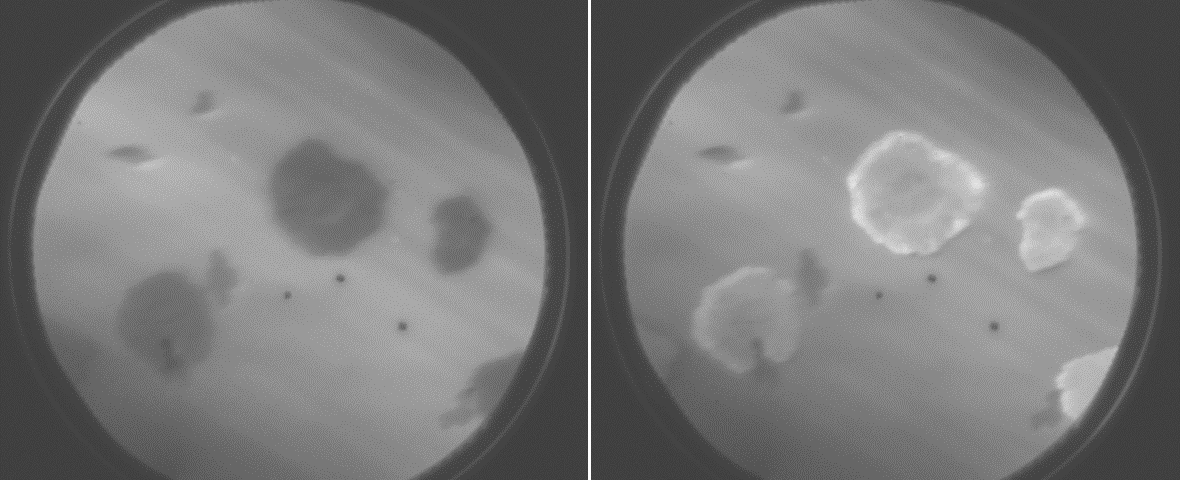 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are stabilized in thin film by epitaxial strains. At elevated temperature, the hexagonal phase transits to the thermodynamically stable orthorhombic phase. Phase coexistence and separation occurs because the transition is the 1st order. Sharp phase boundary is found between the two phases. See more details: Applied Physics Letters 108, 202903, (2016), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are stabilized in thin film by epitaxial strains. At elevated temperature, the hexagonal phase transits to the thermodynamically stable orthorhombic phase. Phase coexistence and separation occurs because the transition is the 1st order. Sharp phase boundary is found between the two phases. See more details: Applied Physics Letters 108, 202903, (2016), arXiv
|
On the structural origin of single ion magnetic anisotropy in LuFeO3
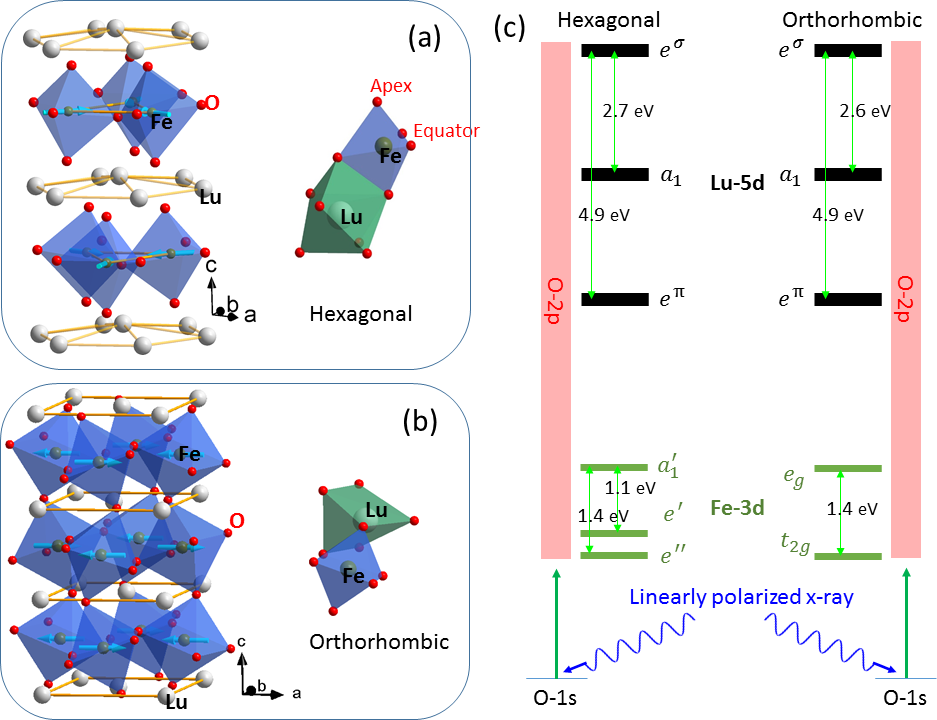 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites simultaneously exhibit spontaneous ferroelectricity and weak ferromagnetisim. The weak ferromagnetism relies on the specific spin anisotropy. We show that it is the subtle structural distorion related to the Fe displacement that generates this anisotropy. See more details: Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 28, 156001, (2016), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites simultaneously exhibit spontaneous ferroelectricity and weak ferromagnetisim. The weak ferromagnetism relies on the specific spin anisotropy. We show that it is the subtle structural distorion related to the Fe displacement that generates this anisotropy. See more details: Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 28, 156001, (2016), arXiv
|
An experimental review of hexagonal rare earth ferrites
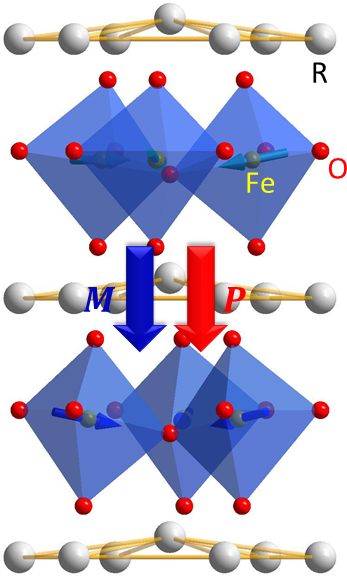 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are a new class of magnetoelectric multiferroic material. They simultaneously exhibit spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations; this suggests promising application in information storage and processing. See more details:Morden Phys. Lett. B 28, 1430008, (2014), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are a new class of magnetoelectric multiferroic material. They simultaneously exhibit spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations; this suggests promising application in information storage and processing. See more details:Morden Phys. Lett. B 28, 1430008, (2014), arXiv
|
Structural origin of the magnetic structure in h-LuFeO3
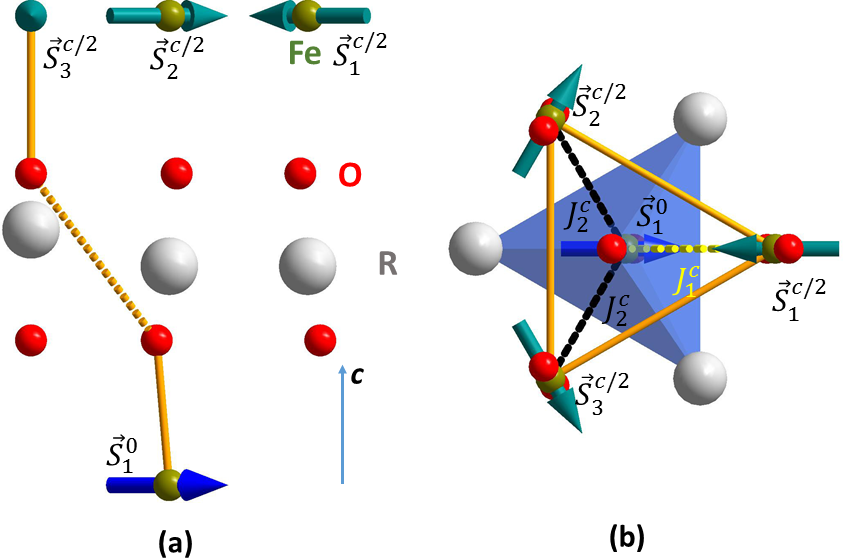 What's the origin of the weak ferromagnetism in h-LuFeO3? Using combined theoretical and experimental studies, we have elucidated that the low temperature weak ferromagnetism originates from a structural change. See more details:Phys. Rev. B. 90, 014436 (2014), arXiv
What's the origin of the weak ferromagnetism in h-LuFeO3? Using combined theoretical and experimental studies, we have elucidated that the low temperature weak ferromagnetism originates from a structural change. See more details:Phys. Rev. B. 90, 014436 (2014), arXiv
|
 High perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), a property needed for nanoscale spintronic applications, is rare in oxide conductors. We report the observation of a PMA up to 0.23 MJ/m3 in modestly strained (–0.3%) epitaxial NiCo2O4 films which are room-temperature ferrimagnetic conductors.
See more details: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 101, 014413 (2020).
High perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA), a property needed for nanoscale spintronic applications, is rare in oxide conductors. We report the observation of a PMA up to 0.23 MJ/m3 in modestly strained (–0.3%) epitaxial NiCo2O4 films which are room-temperature ferrimagnetic conductors.
See more details: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 101, 014413 (2020).
 Substituting rare earth with Sc in RFeO3 results in rich structural phases including orthorhombic, hexagonal, bixbyite, and garnet, as reported in this work.
See more details: J. Appl. Phys. 125, 244101 (2019).
Substituting rare earth with Sc in RFeO3 results in rich structural phases including orthorhombic, hexagonal, bixbyite, and garnet, as reported in this work.
See more details: J. Appl. Phys. 125, 244101 (2019).
 Neutron diffraction on the thin film hexagonal ferrites reveals that working temperature of hexagonal multiferroic ferrites can be increased by reducing size of the R atoms in h-RFeO3 and proves the record-high Neel temperature in h-ScFeO3. The work provides the insight into optimizing hexagonal ferrites by increasing the K3-distortion, which hosts great potential for applications, such as sensors, microwave devices, energy harvesting and energy-efficient recording technologies.
See more details: Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 237203 (2018).
Neutron diffraction on the thin film hexagonal ferrites reveals that working temperature of hexagonal multiferroic ferrites can be increased by reducing size of the R atoms in h-RFeO3 and proves the record-high Neel temperature in h-ScFeO3. The work provides the insight into optimizing hexagonal ferrites by increasing the K3-distortion, which hosts great potential for applications, such as sensors, microwave devices, energy harvesting and energy-efficient recording technologies.
See more details: Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 237203 (2018).
 NiCo2O4 has been revealed as metallic in epitaxial NiCo2O4/MgAl2O4 thin films. However, even with the same optimal growth condition, the NiCo2O4/Al2O3 films are always semiconducting. Using a suite of characterization such as magnetometer, transport, x-ray diffraction, as well as the change of NiCo2O4 upon annealing, we found that the structural disorder caused by the difference between the substrate and the film structures is the origin of the semiconductivity and the large magnetoresistance.
See more details: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51, 145308 (2018).
NiCo2O4 has been revealed as metallic in epitaxial NiCo2O4/MgAl2O4 thin films. However, even with the same optimal growth condition, the NiCo2O4/Al2O3 films are always semiconducting. Using a suite of characterization such as magnetometer, transport, x-ray diffraction, as well as the change of NiCo2O4 upon annealing, we found that the structural disorder caused by the difference between the substrate and the film structures is the origin of the semiconductivity and the large magnetoresistance.
See more details: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51, 145308 (2018).
 Magnetic interactions between Yb and Fe in h-YbFeO3 have been studied. We found that Yb moments follow Fe moments paramagnetically with anti-alignment. At 80 K (moment compensation temperature), the Yb moments and the Fe moments cancel each other. See more details: Phys. Rev. B 95, 224428 (2017).
Magnetic interactions between Yb and Fe in h-YbFeO3 have been studied. We found that Yb moments follow Fe moments paramagnetically with anti-alignment. At 80 K (moment compensation temperature), the Yb moments and the Fe moments cancel each other. See more details: Phys. Rev. B 95, 224428 (2017).
 We have found that h-RFeO3(001)/Fe3O4(111) may form well-defined interface due to good match of lattice constant. It is also interesting that the magnetic easy axis of the two layers are perpendicular to each other: easy axis of Fe3O4 layer in (111) plane; easy axis of h-RFeO3 layer along [001] direction. See more details: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 29, 164001 (2017).
We have found that h-RFeO3(001)/Fe3O4(111) may form well-defined interface due to good match of lattice constant. It is also interesting that the magnetic easy axis of the two layers are perpendicular to each other: easy axis of Fe3O4 layer in (111) plane; easy axis of h-RFeO3 layer along [001] direction. See more details: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 29, 164001 (2017).
 The effect of biaxial strain in hexagonal ferrites has been challenging to tackle due to the experimental difficulties. Employing the restrained thermal expansion method, we successfully measured the strain effect. The results show that the compressive strain enhances the K3 lattice distortion. Our first principle calculation indicate that the compressive strain also enhances the electric polarization bu reduces the magnetic polarization. See more details: Phys. Rev. B. 95, 094110 (2017)
The effect of biaxial strain in hexagonal ferrites has been challenging to tackle due to the experimental difficulties. Employing the restrained thermal expansion method, we successfully measured the strain effect. The results show that the compressive strain enhances the K3 lattice distortion. Our first principle calculation indicate that the compressive strain also enhances the electric polarization bu reduces the magnetic polarization. See more details: Phys. Rev. B. 95, 094110 (2017)
 Fe3O4 is arguably the oldest magnetic material known to the human beings. Yet new functionalities are being exploited constantly. Using the thermal reduction method, we have successfully grown Fe3O4 thin films of flat surface (atomic terrace). See more details: Journal of Applied Physics 120, 085313 (2016), arXiv
Fe3O4 is arguably the oldest magnetic material known to the human beings. Yet new functionalities are being exploited constantly. Using the thermal reduction method, we have successfully grown Fe3O4 thin films of flat surface (atomic terrace). See more details: Journal of Applied Physics 120, 085313 (2016), arXiv
 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are stabilized in thin film by epitaxial strains. At elevated temperature, the hexagonal phase transits to the thermodynamically stable orthorhombic phase. Phase coexistence and separation occurs because the transition is the 1st order. Sharp phase boundary is found between the two phases. See more details: Applied Physics Letters 108, 202903, (2016), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are stabilized in thin film by epitaxial strains. At elevated temperature, the hexagonal phase transits to the thermodynamically stable orthorhombic phase. Phase coexistence and separation occurs because the transition is the 1st order. Sharp phase boundary is found between the two phases. See more details: Applied Physics Letters 108, 202903, (2016), arXiv
 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites simultaneously exhibit spontaneous ferroelectricity and weak ferromagnetisim. The weak ferromagnetism relies on the specific spin anisotropy. We show that it is the subtle structural distorion related to the Fe displacement that generates this anisotropy. See more details: Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 28, 156001, (2016), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites simultaneously exhibit spontaneous ferroelectricity and weak ferromagnetisim. The weak ferromagnetism relies on the specific spin anisotropy. We show that it is the subtle structural distorion related to the Fe displacement that generates this anisotropy. See more details: Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 28, 156001, (2016), arXiv
 Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are a new class of magnetoelectric multiferroic material. They simultaneously exhibit spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations; this suggests promising application in information storage and processing. See more details:Morden Phys. Lett. B 28, 1430008, (2014), arXiv
Hexagonal rare earth ferrites are a new class of magnetoelectric multiferroic material. They simultaneously exhibit spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations; this suggests promising application in information storage and processing. See more details:Morden Phys. Lett. B 28, 1430008, (2014), arXiv
 What's the origin of the weak ferromagnetism in h-LuFeO3? Using combined theoretical and experimental studies, we have elucidated that the low temperature weak ferromagnetism originates from a structural change. See more details:Phys. Rev. B. 90, 014436 (2014), arXiv
What's the origin of the weak ferromagnetism in h-LuFeO3? Using combined theoretical and experimental studies, we have elucidated that the low temperature weak ferromagnetism originates from a structural change. See more details:Phys. Rev. B. 90, 014436 (2014), arXiv