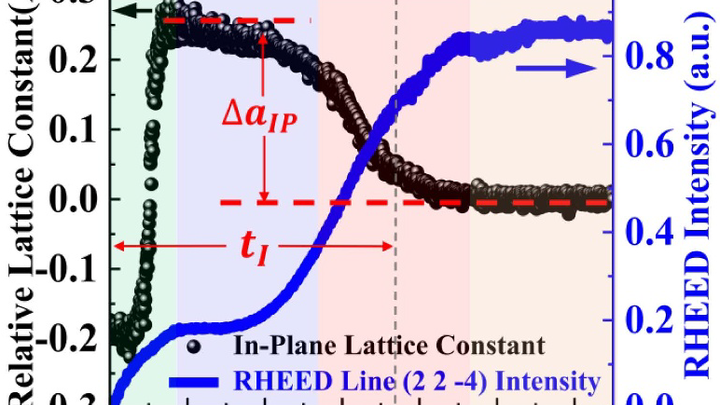
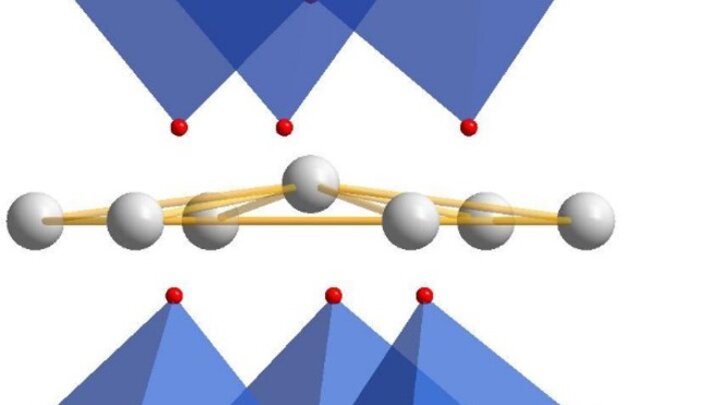
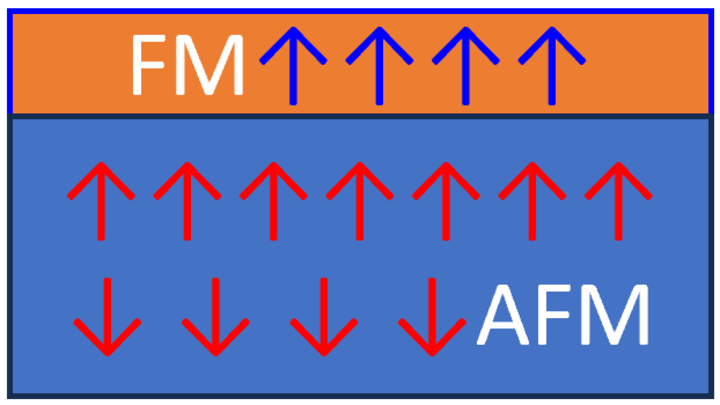
Intrinsic exchange bias is known as the unidirectional exchange anisotropy that emerges in a nominally single-component ferro-(ferri-)magnetic system. In this work, with magnetic and structural characterizations, we demonstrate that intrinsic exchange bias is a general phenomenon in (Ni, Co, Fe)-based spinel oxide films deposited on α-Al2O3(0001) substrates, due to the emergence of a rock-salt interfacial layer consisting of antiferromagnetic CoO from interfacial reconstruction. We show that in NixCoyFe3−x−yO4(111)/α-Al2O3(0001) films, intrinsic exchange bias and interfacial reconstruction have consistent dependences on Co concentration y, while the Ni and Fe concentration appears to be less important. This work establishes a family of intrinsic exchange bias materials with great tunability by stoichiometry and highlights the strategy of interface engineering in controlling material functionalities.
September 30, 2024